Creating Successful Mobile Apps with QA
![James_Govan-CEO[1] James_Govan-CEO[1]](http://www.eolasmagazine.ie/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/James_GovanCEO1_thumb.jpg) Sogeti Ireland CEO James Govan explains how a robust quality assurance process can lower costs and improve time to market.
Sogeti Ireland CEO James Govan explains how a robust quality assurance process can lower costs and improve time to market.
With the prolific adoption of digital devices, the fast-paced trend of government to citizens (G2C), business to business (B2B) and business to consumer (B2C) transactions being conducted on mobiles and tablets continues to grow across all industry sectors.
The ease of use and portability of mobile devices, coupled with the power of ‘apps’, has resonated with both organisations and users alike. It is clear that a great digital experience is no longer a nice-to-have, it is a must-have in order to stay in business and meet ever-increasing user expectations for ease of connectivity and multiple channel access.
Increasingly, mobile (m-business) is disrupting existing industries in exactly the same way the introduction of the web (e-business) did around ten years ago. Think of how Hailo is redefining the taxi industry with its simple, elegant app that is revolutionising how both the service providers (taxi drivers) and users (passengers) interact.
The founders of Hailo set out a clearly defined strategy for their m-business model with a focus on delivering a great user experience and quality solution for their end-users – taxi drivers and passengers. In order to disrupt the market, it was not sufficient just to deliver a functionally rich app, it also needed to have proven high quality characteristics such as performance (rapid response times), reliability (always-on), security (payments) and ease of use (usability).
However, many organisations are still grappling with their digital strategy and approach, particularly those organisations with legacy IT systems which can be difficult to change and enhance to enable ‘appification’ and m-business readiness.
What are the challenges facing your business?
In the frenetic rush to get something out to market quickly, project and software lifecycle shortcuts are often taken which can create a poor user first impression across all measures of quality: poor usability, unreliability, slow performance, security threats and low functionality. In the new digital age, users are very unforgiving of low quality solutions.
How can you face these challenges?
For all organisations making the move to digital, Sogeti’s experience is that essential quality assurance (QA) is involved top-down and end-to-end across all business functions and directly relates to a reduced time to market, lower costs and improved quality and performance. The stakeholders in the digital world include users, partners, marketing, operations and IT among others.
There is a battle under way in many organisations as to which function owns the digital strategy – is it the Chief Marketing Officer (CMO), the CIO or the CTO? – but there is no doubt that it is a topic that has the attention of the C-level in many companies. Regardless of functional ownership, having a well-defined cross-functional quality assurance strategy is essential to ensure m-business solutions are deployed first time and that they work and gain user acceptance and traction.
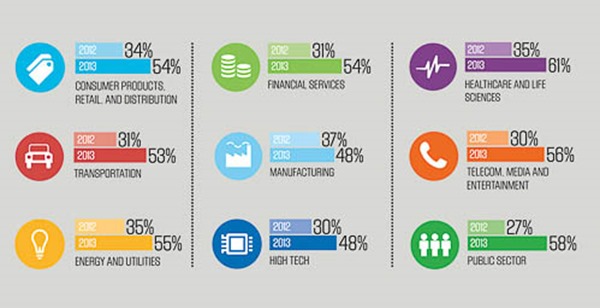
Sogeti’s latest research shows that just over half (55 per cent) of organisations have introduced mobile testing practices in 2013, which is significantly up on last year’s figure (31 per cent).
However, it is a common myth that testing functionality on mobile is sufficient in itself. It is not. Functional testing is only aimed at finding defects and is a small subset of the over-arching QA strategy needed to deliver quality mobile solutions.
It is imperative that organisations devise an appropriate mobile QA strategy that covers the end-to-end lifecycle from development to deployment and considers quality characteristics beyond pure functionality such as usability, performance and security.
What steps can you take?
Sogeti recommends that the following QA disciplines are included with your functional mobile testing to ensure your organisation has a robust and adequate approach in place.
Installation and launch testing: Recent studies show that 60 per cent of mobile users will abandon your app or site if it doesn’t load within three seconds. It is critical that you have a test approach that checks that your app and mobile solutions correctly install and launch on the target deployment platform and devices.
Device compatibility testing: With multiple platforms (phone, tablet), multiple operating systems (iOS, Android, Windows, Blackberry) and communications service providers (carriers) forming part of the deployment eco-system, it can be difficult to test on all combinations. Using emulators offers some benefits but the only true test is to conduct it on real devices and over a real carrier network. A proper automation approach is a must to ensure repeatable and cost-effective testing.
Performance testing and optimisation: There are many testing issues to consider here but the main items are:
• connection speed – check how your app performs in wi-fi, 3G and 4G networks;
• data usage – an increasing problem for both carriers and users (badly designed apps make inefficient use of the carrier’s network resources and reduce performance, and poorly developed apps generate extraneous data for users who then incur higher than necessary usage charges); and
• battery usage – this might surprise to have it listed here but fast battery drain is one of the major issues with badly developed apps and a major cause of user dissatisfaction.
Usability testing: This is critically important to test the user interface and user interaction with the app to ensure a high quality user experience. Mobile users want to start using their new apps quickly. If logging in and navigation is not easy or intuitive, then they are most likely to discard it after first usage.
Security testing: This covers a wide range of issues including data confidentiality, user authentication, user authorisation, data retention and malware vulnerabilities. This is one of the least developed areas of testing within most organisations.
Compliance testing: This can be considered in two areas.
Firstly, legislative compliance. Governments, government agencies and legislators around the world are struggling to keep legislation up to date with the rapid pace of change in mobile apps and m-business. Organisations such as the US Federal Trade Commission (FTC) have documented guidelines on how organisations must comply with advertising standards and restricting mobile app services for children (www.onguardonline.gov/mobileapps). Your QA organisation must be familiar with such legislation and guidelines and have tests in place to validate compliance.
Secondly, app marketplace compliance. The major players (AppStore, Android Marketplace, Windows Marketplace, Blackberry AppWorld) all have checklists that must be complied with before mobile apps can be uploaded for distribution. These checklists are extensive, updated on a very frequent basis, and your QA team needs to keep abreast of the compliancy requirements.
Mobile is the future
The importance of quality assurance cannot be overstated when you are implementing a digital strategy for your organisation. Companies which are leveraging QA leading practice, processes and tools for their mobile apps and m-business solutions are gaining competitive advantage as they are delivering quality solutions to the marketplace.
As the market for mobile solutions continues to grow exponentially, organisations which make real-world testing coverage and QA a priority will be rewarded with greater market share, user loyalty and increased profitability. In the future, your business may not just be about ensuring your products and services are accessible on mobile. As Hailo has demonstrated, mobile may be your business.
 James can be contacted as follows:
James can be contacted as follows:
Tel: +353 (0)1 639 0163
Mobile: +353 (0)86 8372365
Email: james.govan@sogeti.com